Understanding English Tenses: A Comprehensive Guide with Tense Chart, Rules & Examples
A tense chart provides a structured way to understand English verb tenses, displaying the different forms verbs take depending on time. It helps learners visualize tense usage, making it easier to grasp how verbs change to express different times, actions, and conditions in speech and writing.
What Are Tenses?
In English grammar, tenses are essential verb forms that indicate when an action or situation happens—whether in the past, present, or future. According to the Oxford Dictionary, a tense is “any of the forms of a verb that indicate the time of an action or state expressed by the verb.” By using auxiliary verbs like “be,” “have,” and “will,” we can structure sentences to show exactly when something occurs.
Types of Tenses in English
English tenses are grouped into three main types:
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
Each of these main tenses has subcategories—simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous—allowing us to communicate actions and states with precision. Whether you’re aiming for accuracy in speaking or writing, a clear understanding of tenses ensures effective expression.
Expanded Explanation of Tenses in English
Mastering the tenses in English is essential for clear and effective communication, as it allows speakers and writers to convey when an action occurs. Tenses are categorized into three primary types: Present, Past, and Future. Each type is further divided into Simple, Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous forms, resulting in a total of twelve main tenses.
Simple Tenses
- Present Simple Tense: This tense is used to express habitual actions, general truths, or fixed arrangements.
- Example: “She wakes up early every morning.”
- Formula: Subject + Base form of verb (or -s/-es for third person singular) + rest of sentence.
- Past Simple Tense: Used to describe actions completed in the past at a specific time.
- Example: “They played cricket yesterday.”
- Formula: Subject + Past form of verb + rest of sentence.
- Future Simple Tense: Indicates an action that will take place in the future.
- Example: “I will go to school tomorrow.”
- Formula: Subject + will/shall + Base form of verb + rest of sentence.
Continuous (Progressive) Tenses
- Present Continuous Tense: This tense indicates actions that are occurring at the exact time of speaking.
- For example: “They are currently playing cricket as practice for the tournament.”
- Formula: Subject + am/is/are + Verb + ing + rest of sentence.
- Past Continuous Tense: Used to describe actions that were ongoing at a specific past time.
- Example: “She was playing cricket when I called her.”
- Formula: Subject + was/were + Verb + ing + rest of sentence.
- Future Continuous Tense: Refers to actions that will be in progress at a particular time in the future.
- Example: “I will be working late tomorrow.”
- Formula: Subject + will be/shall be + Verb + ing + rest of sentence.
Perfect Tenses
- Present Perfect Tense: Describes actions that occurred at an indefinite time in the past and are relevant to the present.
- Example: “He has lived in this city for four years.”
- Formula: Subject + have/has + Past participle + rest of sentence.
- Past Perfect Tense: Used for actions completed before another past action or time.
- Example: “She had already eaten when he arrived.”
- Formula: Subject + had + Past participle + rest of sentence.
- Future Perfect Tense: Refers to actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
- Example: “By this time next month, they will have finished their project.”
- Formula: Subject + will have/shall have + Past participle + rest of sentence.
Perfect Continuous Tenses
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense: Emphasizes the duration of an ongoing action that started in the past and continues to the present.
- Example: “I have been studying all day.”
- Formula: Subject + have/has + been + Verb + ing + rest of sentence.
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Describes actions that were ongoing in the past before another action.
- Example: “He had been working on the project when the deadline was extended.”
- Formula: Subject + had + been + Verb + ing + rest of sentence.
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense: Indicates actions that will continue up to a specific time in the future.
- Example: “By next year, she will be teaching for ten years.”
- Formula: Subject + will have been + Verb + ing + rest of sentence.
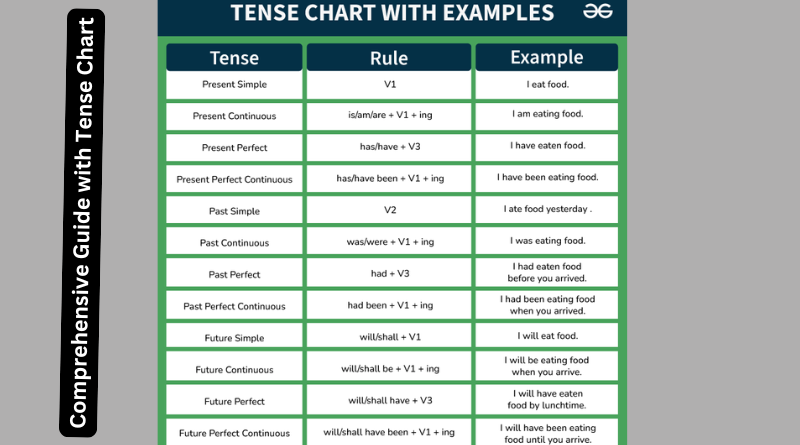
Summary Chart of Tenses
| Tense Type | Example Sentence | Formula |
| Present Simple | She wakes up early every morning. | Subject + Base form of verb + rest |
| Past Simple | They played cricket yesterday. | Subject + Past form of verb + rest |
| Future Simple | I will go to school tomorrow. | Subject + will/shall + Base form + rest |
| Present Continuous | They are playing cricket now. | Subject + am/is/are + Verb + ing + rest |
| Past Continuous | She was playing cricket when I called. | Subject + was/were + Verb + ing + rest |
| Future Continuous | I will be working late tomorrow. | Subject + will be/shall be + Verb + ing |
| Present Perfect | He has lived here for four years. | Subject + have/has + Past participle |
| Past Perfect | She had already eaten when he arrived. | Subject + had + Past participle |
| Future Perfect | They will have finished by next month. | Subject + will have/shall have + Participle |
| Present Perfect Continuous | I have been studying all day. | Subject + have/has + been + Verb + ing |
| Past Perfect Continuous | He had been working when she came. | Subject + had + been + Verb + ing |
| Future Perfect Continuous | She will have been teaching a year by then. | Subject + will have been + Verb + ing |
Understanding these tenses in depth will empower you to express events and actions more clearly and accurately, enhancing communication skills in both speech and writing.
Utilizing the Tense Chart
To effectively use the Tense Chart, follow these essential steps:
- Check the Time Frame: Begin by identifying when the action occurs. The sentence “By next year, she will be teaching for ten years” is in the future tense. Understanding the time frame is crucial for selecting the correct tense.
- Select the Appropriate Tense: Once you’ve established the time frame, choose the relevant tense that fits the context of your sentence. Different actions and states require different tenses for clarity and accuracy.
- Construct Sentences: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the selected tense. Identify the main verbs, the appropriate verb forms, and any necessary adverbs or prepositions that complete the sentence.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering verb tenses. Engage in exercises that require you to apply different tenses in various contexts. The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with using tenses correctly in both speech and writing.
Conclusion
Understanding verb tenses is fundamental for effective communication in English. The Tense Chart serves as a valuable tool that organizes various tenses and helps learners grasp the nuances of expressing time in language. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of tenses—present, past, and future—as well as their various forms, you can enhance your writing and speaking skills. Mastery of tenses not only improves clarity but also boosts your confidence in everyday interactions.
As you practice using the Tense Chart and implementing the appropriate tenses in your sentences, you’ll find that expressing yourself becomes more precise and meaningful. Remember, consistent practice and application are essential to solidifying your understanding of English tenses, ultimately leading to more effective communication. Embrace the learning process, and you’ll soon find yourself navigating the complexities of verb tenses with ease.